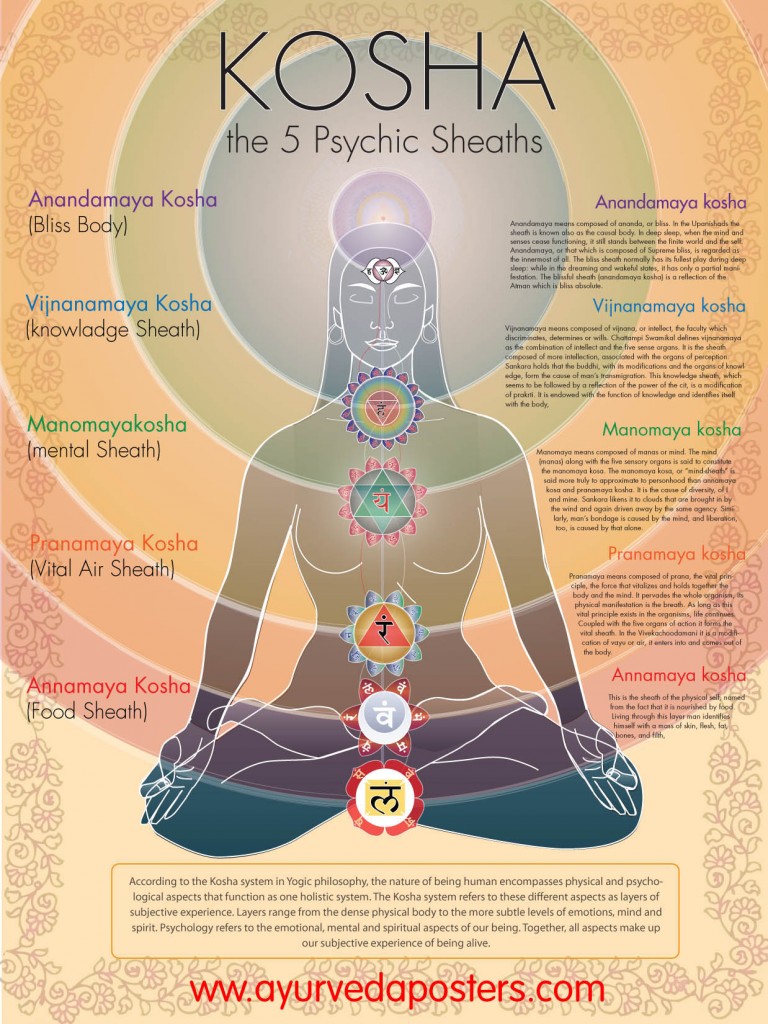
This blog explores whether Advaita Vedānta and Buddhism ultimately point to the same truth. Through a thoughtful dialogue, it traces the meeting ground between Nāgārjuna’s emptiness (śūnyatā) and Gaudapāda’s non-origination (ajāti). Both dissolve all dualities—self and other, subject and object—revealing an unborn reality beyond thought. Yet a tension remains: Buddhism denies any enduring consciousness, while Advaita proclaims consciousness alone as the timeless reality.
As the conversation deepens, these apparent opposites begin to merge. When both experiencer and experienced vanish, is “emptiness” truly different from “consciousness”? The article suggests that Gaudapāda, writing before sectarian walls were built, may have seen the essential convergence between these paths.
Ultimately, this piece—arising from a dialogue with Claude AI—reflects the timeless exchange between Buddhist and Advaitin inquiry, showing how both, when followed to their limit, dissolve into the same wordless recognition of non-dual truth beyond affirmation or negation.